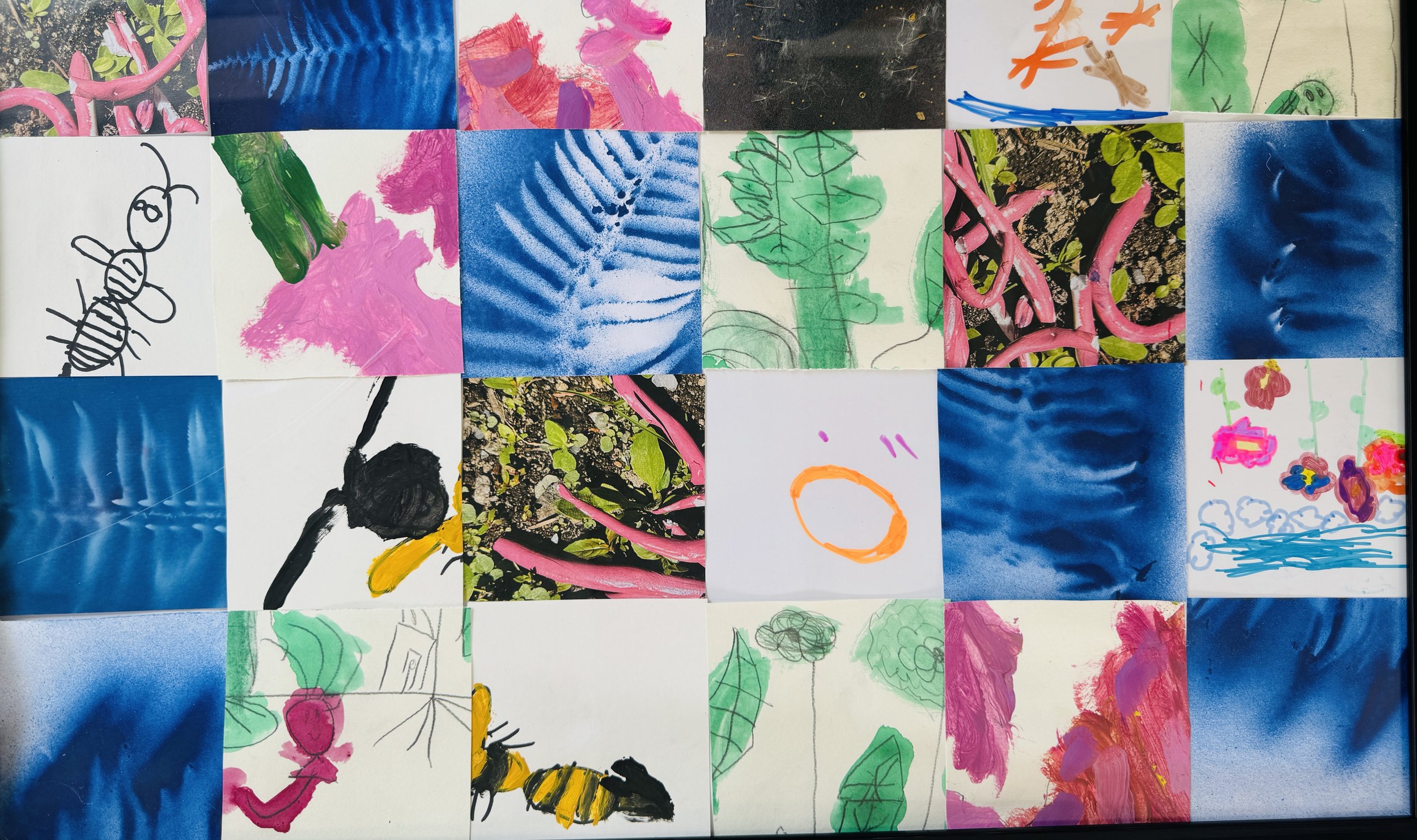
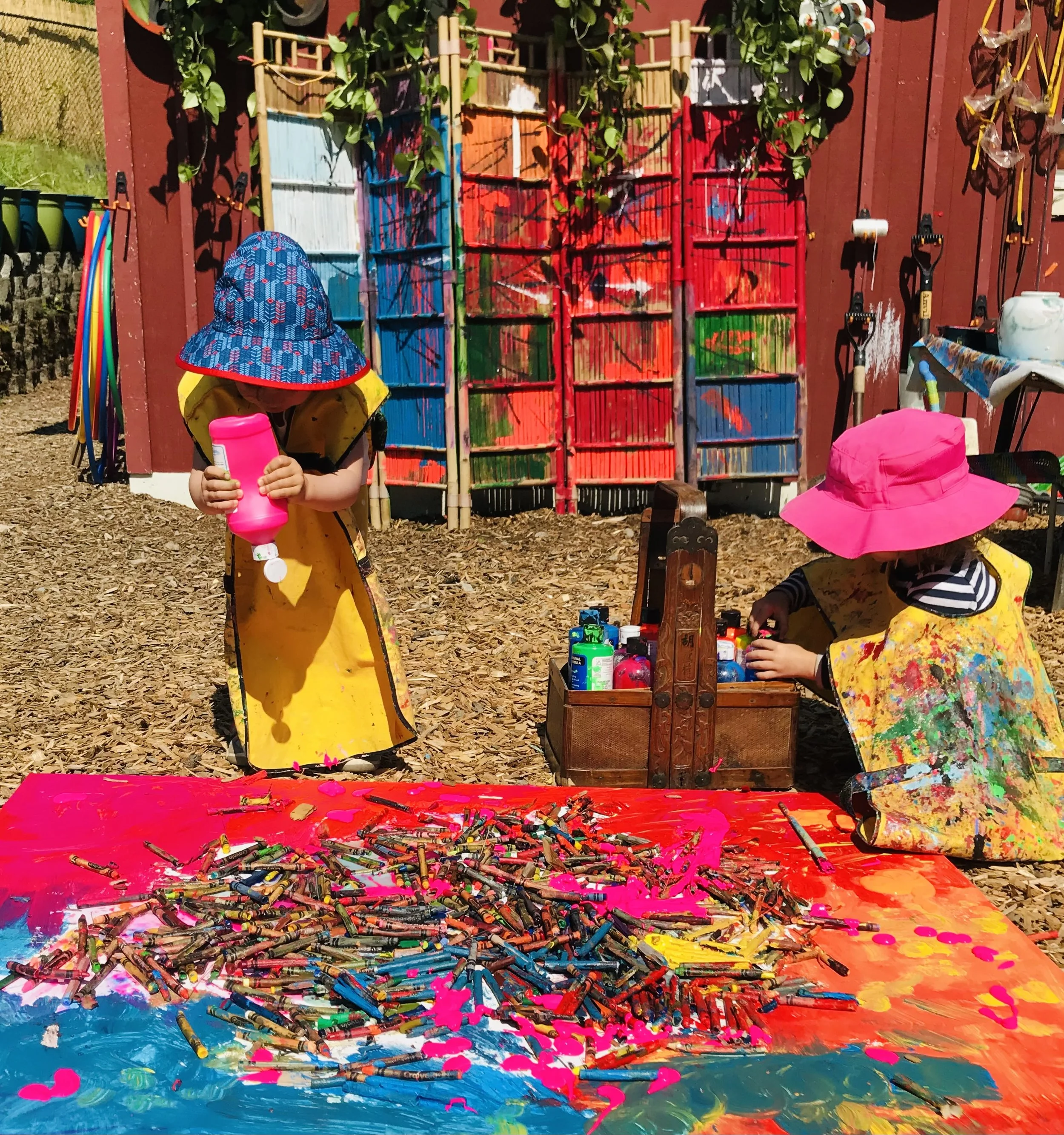
PreK 1 Program Overview
Teacher-Student Ratio 1:7 (max)
Class Size: 20 Students/class (max)
Curriculum: The PreK 1 Curriculum occurs in an 80% Mandarin immersion environment. The students have core curricular classes and specialty classes each week, along with 2 hours of meal & playtime.
The curriculum also includes ongoing enrichment, a hallmark feature of our elementary program.
Language Ratio: Mandarin 80%, English 10%, Spanish 10%
Learn more about Sky + Sea Dragon Teachers
Sample Schedule
Students in the Panda Classroom are formally assessed 3 times a year on a developmental scale. These robust benchmarks measure everything from expressive speech to gross motor development.
PreK 1 Learning at IFS
Welcome to our PreK 1 program, where we embrace the Reggio Emilia approach, focusing on self-directed exploration and discovery. Our nurturing environment sparks creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving through hands-on learning and open-ended play.
Personalized Development - Executive Functioning
Through Differentiated Executive Functioning Tasks, we support each child's unique development. Our educators tailor activities to build essential skills such as attention, memory, flexibility, and self-control, empowering our young learners to thrive. Students become faster at problem solving and understanding that there are often multiple pathways towards finding answers.
Outdoor Play, Rain or Shine
We believe in the importance of outdoor play every day. Our spacious play areas feature age-appropriate equipment and sensory gardens, allowing children to develop gross motor skills, build resilience, and learn from diverse sensory experiences. Our spacious play areas and weekly trips to the Bellevue Botanical Gardens let children connect with nature and explore the world around them.
Independence and Self-Confidence
Our teachers guide and support children as they take on challenges, make choices, and take ownership of their learning, fostering autonomy and a lifelong love of learning. Our PreK 1 classroom is a joyful place for young learners.
Social-Emotional Growth
We model and encourage kindness, empathy, and effective communication. Through cooperative play and guided discussions, children learn to express feelings, resolve conflicts, and build lasting friendships in a safe and inclusive environment, nurturing essential skills for success in school and beyond.
Core Subjects
-
Curriculum Resources:
In the PreK1 Class, students begin to recognize and read around 30.
The teacher will bring in comprehensive vocabulary based on the emergent curriculum.
Students who are already Mandarin proficient receive extra support in English.
-
Our PreK1 Mathematics program is a robust exploration into both Executive Functioning Skills and early math skill practice.
Basic Standards:
Number Recognition and Counting
Recognize and name numbers 0-10
Count objects up to 10 reliably
Basic Shapes
Identify and name basic shapes (circle, square, triangle, rectangle)
Sorting and Classifying
Sort objects by one attribute (color, size, or shape)
Patterns
Recognize and continue simple patterns (AB patterns)
Measurement
Compare objects using terms like bigger/smaller, longer/shorter
Positional Words
Understand and use words like above, below, next to, behind
Advanced Standards:
Extended Number Sense
Recognize and name numbers up to 20
Count objects up to 20 reliably
Understand the concept of zero
Introduction to Addition and Subtraction
Add and subtract within 5 using concrete objects
Advanced Shapes
Identify and name more complex shapes (oval, diamond, hexagon)
Combine shapes to form new shapes
Advanced Patterns
Create and extend more complex patterns (ABC, AAB patterns)
Measurement and Comparison
Use non-standard units to measure length (e.g., paper clips, cubes)
Compare and order objects by weight or capacity
Data and Graphing
Collect and represent simple data using objects or pictures
Time Concepts
Understand basic time concepts (morning, afternoon, night)
Recognize that clocks and calendars measure time
Problem Solving
Solve simple word problems using objects or drawings
Early Fraction Concepts
Understand basic concepts of "whole" and "half" using concrete objects
-
Project Based Learning has profound influence on a child's genuine interest in learning. Some of the main benefits are described below.
Engagement and Motivation
Increases student interest and enthusiasm for learning
Makes learning more meaningful and relevant to real-life experiences
Develops Critical Thinking Skills
Encourages problem-solving and decision-making
Promotes analytical thinking from an early age
Enhances Creativity
Allows children to explore and express ideas in various ways
Fosters innovative thinking and imagination
Improves Communication Skills
Provides opportunities for verbal expression and listening
Encourages sharing ideas and collaborating with peers
Builds Teamwork and Social Skills
Teaches cooperation and conflict resolution
Develops empathy and respect for others' ideas
Promotes Self-Directed Learning
Encourages children to take initiative in their learning
Builds confidence and independence
Integrates Multiple Subjects
Combines different areas of learning (e.g., math, science, art) in meaningful ways
Helps children see connections between different concepts
Develops Fine and Gross Motor Skills
Involves hands-on activities that improve physical coordination
Enhances skills like cutting, drawing, and constructing
Fosters Emotional Intelligence
Helps children manage frustration and celebrate achievements
Builds resilience and perseverance
Encourages Family Involvement
Creates opportunities for parents to engage in their child's learning
Strengthens school-home connections
-
Letter Recognition
Recognize and name most uppercase and lowercase letters of the alphabet
Letter-Sound Correspondence
Begin to associate letters with their most common sounds
Identify the beginning sound of familiar words
Print Awareness
Understand that print carries meaning
Recognize that English text is read from left to right and top to bottom
Parts of a Book
Identify the front cover, back cover, and title page of a book
Understand the roles of author and illustrator
Book Handling
Hold a book correctly and turn pages from front to back
Concepts of Print
Recognize that words are separated by spaces
Understand that sentences start with a capital letter and end with a period
Phonological Awareness
Recognize and produce rhyming words
Segment spoken words into syllables
Vocabulary Development
Use and understand new words learned from conversations and books
Begin to use descriptive words in speech
Comprehension
Answer simple questions about a story that has been read aloud
Retell familiar stories using beginning, middle, and end
Writing
Write some letters of the alphabet, especially those in their name
Use drawings, dictation, and early writing to express ideas
Listening and Speaking
Follow simple, multi-step directions
Participate in conversations and share ideas
Story Elements
Identify main characters in a story
Recognize basic settings (e.g., home, school, park)
-
Curriculum Resources:
Teachers use Everyday Speech to guide First Graders through their idaily SEL Class.
Certainly. Here are standards for socio-emotional learning (SEL) appropriate for PreK 1 students:
Self-Awareness
Recognize and name basic emotions (happy, sad, angry, scared)
Identify personal likes and dislikes
Self-Regulation
Use simple strategies to calm down when upset (e.g., deep breathing, counting)
Follow classroom rules and routines
Social Awareness
Recognize others' feelings through facial expressions and body language
Show empathy towards peers and adults
Relationship Skills
Take turns and share with others
Use words to express needs and wants
Responsible Decision-Making
Make simple choices and explain reasoning
Understand consequences of actions
Emotional Vocabulary
Learn and use words to describe different feelings
Express emotions verbally instead of physically
Conflict Resolution
Use simple problem-solving steps with adult guidance
Learn to apologize and make amends
Cooperation
Work and play cooperatively in small groups
Participate in collaborative activities
Self-Esteem
Recognize personal strengths
Show confidence in attempting new tasks
Diversity and Inclusion
Recognize and respect differences in others
Include others in play and activities
Personal Space and Boundaries
Understand and respect personal space
Ask permission before touching others
Kindness and Compassion
Perform simple acts of kindness
Show care for classmates who are upset
Persistence and Resilience
Continue trying when facing challenges
Ask for help when needed
Self-Care
Practice basic hygiene routines
Recognize the importance of rest and healthy eating
Community Awareness
Understand their role in the classroom community
Participate in simple community service projects
Specialty Subjects
-
Here are five fundamental physical education standards for PreKindergarten students:
Gross Motor Skills Development: Students will demonstrate competency in fundamental gross motor skills, such as running, jumping, hopping, galloping, skipping, and sliding.
Body and Spatial Awareness: Students will develop an understanding of their own bodies and how they move through space, demonstrating the ability to navigate their environment safely and effectively.
Balance and Coordination: Students will engage in activities that promote balance and coordination, such as walking on a balance beam, standing on one foot, or participating in simple yoga poses.
Object Manipulation: Students will develop skills in manipulating various objects, such as throwing and catching balls, kicking, rolling, and striking objects with hands or simple equipment.
Cooperative Play and Sportsmanship: Students will participate in cooperative games and activities that encourage teamwork, sharing, turn-taking, and good sportsmanship, fostering positive social interactions and emotional development.
-
Basic Standards:
Color Recognition
Identify and name primary colors
Mix primary colors to create secondary colors
Shape and Form
Recognize and draw basic shapes (circle, square, triangle)
Create simple forms using playdough or clay
Line
Draw different types of lines (straight, curved, zigzag)
Use lines to create simple pictures
Texture
Explore and describe different textures (smooth, rough, bumpy)
Create rubbings to capture textures
Fine Motor Skills
Hold and use crayons, markers, and paintbrushes correctly
Practice cutting with safety scissors
Advanced Standards:
Color Theory
Introduce the concept of warm and cool colors
Experiment with color mixing to create shades and tints
Composition
Understand basic concepts of foreground and background
Create artwork that fills the entire space
Art Appreciation
Look at and discuss works of art
Express preferences for different artworks
Multi-media Art
Combine different materials in artwork (e.g., paint and collage)
Explore digital art tools under supervision
Art and Emotions
Use colors and shapes to express feelings in artwork
Discuss how artwork makes them feel
Cultural Art Awareness
Explore art from different cultures
Create art inspired by cultural traditions
3D Art
Create simple sculptures using various materials
Understand the difference between 2D and 3D art
Observational Drawing
Draw simple objects from observation
Notice and depict basic details in subjects
Art and Nature
Use natural materials in art projects
Create art inspired by nature
Creative Expression
Use art to tell stories or express ideas
Experiment with unconventional art tools (e.g., sponges, string)
-
Certainly! Here are STEAM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, and Mathematics) standards for PreK 1, integrating these disciplines in an age-appropriate manner:
Science:
Scientific Inquiry
Ask questions about the natural world
Make simple observations using senses
Living Things
Identify basic needs of plants and animals
Observe and describe changes in living things
Earth and Space
Recognize basic weather patterns
Explore properties of rocks, soil, and water
Technology: 4. Digital Awareness
Identify common technology devices
Understand basic functions of digital tools (e.g., on/off, volume)
Simple Machines
Explore and use simple machines (e.g., ramps, levers)
Understand how tools help us do work
Engineering: 6. Design Process
Plan and create simple structures
Test and improve designs
Problem Solving
Identify simple problems in daily life
Brainstorm solutions using available materials
Art: 8. Creative Expression
Use various materials to create art
Express ideas through visual arts
Artistic Techniques
Explore different art-making techniques
Mix colors and create textures
Mathematics: 10. Number Sense - Count objects up to 20 - Understand one-to-one correspondence
Patterns and Relationships
Recognize and create simple patterns
Sort objects based on attributes
Integrated STEAM: 12. Nature and Art - Create art using natural materials - Observe and draw plants or animals
Building and Construction
Use blocks or recycled materials to build structures
Explore balance and stability in constructions
Measurement and Comparison
Use non-standard units to measure objects
Compare sizes, weights, and capacities
Environmental Awareness
Participate in simple recycling activities
Learn about conservation of resources
-
Basic Standards:
Singing
Sing simple songs in a group
Match pitch within a limited range
Rhythm
Clap or tap simple rhythms
Move to a steady beat
Listening
Recognize different types of sounds (loud/soft, high/low)
Identify common instruments by sound (e.g., piano, drum, guitar)
Musical Play
Engage in musical games and finger plays
Use body movements to express music
Instruments
Explore and play simple classroom instruments (e.g., shakers, bells)
Advanced Standards:
Vocal Expression
Experiment with different voice types (speaking, singing, whispering)
Create vocal sound effects for stories or songs
Advanced Rhythm
Recognize and reproduce simple rhythm patterns
Differentiate between fast and slow tempos
Music and Emotions
Express how different types of music make them feel
Use music to tell simple stories
Music Notation
Introduce very basic notation concepts (e.g., notes go up when pitch goes up)
Create simple pictorial representations of sounds or music
Cultural Music Awareness
Experience music from different cultures
Recognize that music is used in various ways in daily life
Composition
Create simple musical phrases using voice or instruments
Improvise responses to musical prompts
Music and Movement
Perform simple dances or choreographed movements to music
Use creative movement to interpret different musical elements
Dynamics
Understand and demonstrate the concepts of loud and soft in music
Control volume while singing or playing instruments
Music Appreciation
Listen attentively to short musical pieces
Express preferences for different types of music
Music and Other Arts
Explore connections between music and other art forms (e.g., drawing to music)
-
PreK 1 Students at IFS begin to work before they play: raking leaves, watering plants and helping in the garden.
-
PreK 1 Students walk to the park every Thursday in rain or shine from the first week of school.
They also have an organized Field Trip to a well -known farm, museum or hiking trip.
Exploring Powerful Interactions:
Project Based Learning in PreK 1
-
Here are some ways that IFS applies simple math standards to this project:
Counting and Number Recognition
Count the number of petals on different flowers
Count the number of legs on various animals
Recognize and identify numbers on plant pots or animal habitats
Sorting and Classifying
Sort plants by size (small, medium, large)
Classify animals by their habitats (land, water, air)
Patterns
Create patterns with different types of leaves or flowers
Identify patterns in animal markings (e.g., stripes on a tiger)
Measurement
Measure plant growth using non-standard units (e.g., paper clips)
Compare sizes of different animals using terms like bigger/smaller
Shapes
Identify shapes in plants (e.g., circular flowers, triangular leaves)
Recognize basic shapes in animal body parts
Graphing
Create a simple pictograph of favorite plants or animals in the class
Make a bar graph showing the number of seeds planted in different pots
Estimation
Estimate how many seeds are in a fruit
Guess how many animals might live in a specific habitat
Simple Addition and Subtraction
Add the number of plants in two different areas of a garden
Subtract leaves that fall from a plant
Comparisons
Compare quantities of different types of plants or animals
Order animals from smallest to largest
Data Collection
Collect and record data on plant growth over time
Track the number of different animals observed during a nature walk
-
Although these might change, the common standards for this project are:
Vocabulary Acquisition
Learn basic plant names (树 - tree, 花 - flower, 草 - grass)
Learn common animal names (猫 - cat, 狗 - dog, 鸟 - bird)
Character Recognition
Recognize simple characters related to nature (木 - wood, 田 - field)
Identify the character 动 in 动物 (animal)
Pinyin Introduction
Learn the pinyin for basic colors found in nature (绿 lǜ - green, 棕 zōng - brown)
Practice pronouncing animal sounds in Mandarin (喵 miāo - meow, 汪 wāng - woof)
Simple Phrases
Use the phrase "这是..." (zhè shì... - This is...) to identify plants and animals
Learn "我喜欢..." (wǒ xǐhuān... - I like...) to express preferences
Counting
Count plants or animals using Mandarin numbers (一 yī, 二 èr, 三 sān)
Use measure words like 只 (zhī) for animals and 棵 (kē) for trees
Basic Strokes
Practice writing simple strokes found in nature-related characters
Trace characters like 山 (shān - mountain) or 水 (shuǐ - water)
Listening Comprehension
Follow simple instructions in Mandarin related to caring for plants or animals
Understand basic descriptions of plants or animals
Speaking Practice
Describe a plant or animal using simple adjectives (大 dà - big, 小 xiǎo - small)
Role-play being different animals and make their sounds in Mandarin
Cultural Connection
Learn about animals in Chinese zodiac (生肖 shēngxiào)
Introduce plants significant in Chinese culture (like 竹 zhú - bamboo)
Song and Rhyme
Learn simple songs about plants or animals in Mandarin
Practice rhymes that include nature vocabularyDescription text goes here
-
These science standards are typically covered with the PreK 1 unit on Plants + Animals.
Living vs. Non-living: Students will distinguish between living things (plants and animals) and non-living objects in their environment.
Basic Needs: Children will identify the basic needs of plants and animals (food, water, air, shelter).
Plant Parts: Students will recognize and name the main parts of a plant (roots, stem, leaves, flower).
Animal Characteristics: Children will identify basic characteristics of animals (e.g., fur, feathers, scales) and how they move.
Life Cycles: Students will observe and describe simple life cycles of plants (seed to plant) and animals (egg to butterfly).
Habitats: Children will recognize that different plants and animals live in different environments (e.g., water, land, air).
Plant and Animal Interactions: Students will understand simple ways plants and animals depend on each other (e.g., bees pollinating flowers, birds eating seeds).
These standards provide a foundation for understanding basic concepts about plants and animals, appropriate for PreK 1 students. They focus on observation, identification, and simple relationships in nature.
Investigations into Living Things
Traces of what is left behind
Exploring Water-Based Ecosystems + Habitats
-
Each water based ecosystem will have slightly different standards, but these are the most commonly explored standards:
Properties of Water
Observe and describe the basic properties of water (e.g., it's wet, can flow, takes the shape of its container)
Recognize that water can exist in different forms (liquid, ice, steam)
States of Matter
Identify water in its three states: solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (steam)
Observe how water changes from one state to another (e.g., melting, freezing)
Buoyancy
Predict and test which objects will sink or float in water
Explore how shape affects an object's ability to float
Water Cycle
Introduce basic concepts of evaporation and condensation
Observe water disappearing (evaporating) and reappearing (condensing)
Surface Tension
Observe how water forms droplets
Explore how some insects can walk on water
Absorption
Investigate which materials absorb water and which don't
Compare the absorbency of different materials
Water as a Solvent
Observe how some substances dissolve in water
Explore mixing and separating water with other materials
Water Movement
Observe how water moves (flows downhill, forms rivers)
Explore concepts of pouring and dripping
Water Conservation
Understand that water is a limited resource
Learn simple ways to save water
Water and Living Things
Recognize that plants and animals need water
Observe how plants absorb water
Water and Weather
Identify different forms of precipitation (rain, snow, hail)
Understand that clouds are made of water
Simple Machines and Water
Introduce simple water tools (e.g., water wheels, pumps)
Explore how water can be used to move things
-
These are commonly used math standards that engage our PreK 1 students during their study of water.
Counting and Cardinality
Count water drops, objects that sink or float
Recognize numerals on measuring cups or containers
Number Recognition
Match number of water drops to numerals
Identify numbers on water-related tools and containers
Measurement (including Volume and Weight)
Compare volumes of water in different containers
Measure rainfall using simple rain gauges
Explore weight of water-filled containers
Compare weights of different objects in water
Use non-standard units to measure water (e.g., cups, spoons)
Estimation
Estimate how many cups will fill a larger container
Guess how long it will take for ice to melt
Predict the weight of water-filled containers
Shapes
Identify shapes of various containers
Observe how water takes the shape of its container
Patterns
Create patterns with water drops or ice cubes
Identify patterns in water ripples
Sorting and Classifying
Sort objects that sink or float
Classify water sources (rivers, lakes, oceans)
Graphing
Create simple bar graphs of sink/float results
Make pictographs of favorite water activities
Comparison
Compare weights and volumes of containers with different amounts of water
Order containers from least to most full
Simple Addition and Subtraction
Add drops of water to a container
Subtract water as it evaporates
Time Concepts
Measure time it takes for ice to melt
Observe daily water routines (e.g., watering plants)
Data Collection
Record daily water usage
Track plant growth with different amounts of water
Spatial Relationships
Use positional words to describe floating objects (on top, under)
Arrange water containers in different configurations
One-to-One Correspondence
Match one cup to each plant when watering
Pair each boat with a body of water on a map
Symmetry
Observe symmetry in water reflections
Create symmetrical water drop patterns
Activities integrating multiple standards:
Sink or Float Experiment: Predict, test, count, and graph objects that sink or float.
Water Measurement Station: Use different-sized containers to measure, compare, and order volumes of water.
Ice Melting Time: Estimate and measure the time it takes for ice cubes to melt under different conditions.
Rain Gauge Project: Make simple rain gauges, measure rainfall, and create graphs of the data.
Water Cycle in a Bag: Observe and measure water as it evaporates and condenses in a sealed bag.
Plant Watering Math: Measure water for plants, count days between watering, and track growth.
Water Conservation Chart: Count and graph ways to save water at home and school.
Buoyancy Balance: Use a balance scale to compare weights of objects in and out of water.Description text goes here
-
These Mandarin standards are taught in each Water Project in Trimester 2:
Certainly! Here are Mandarin Literacy standards that can be integrated into a Water Project for PreK 1 students:
Vocabulary Acquisition
Learn basic water-related words: 水 (water), 雨 (rain), 冰 (ice)
Introduce simple verbs: 喝 (drink), 流 (flow), 冻 (freeze)
Character Recognition
Recognize the character 水 (water) in different contexts
Identify water-related radicals like 氵(three-dot water radical)
Pinyin Introduction
Learn the pinyin for water-related words
Practice tones using water sounds (e.g., drip, splash)
Simple Phrases
Use "这是..." (This is...) to identify water in different forms
Learn "我喜欢..." (... - I like...) to express preferences about water activities
Counting in Water Context
Count water drops or containers using Mandarin numbers
Use measure word 滴 for drops of water
Basic Strokes
Practice writing strokes found in water-related characters
Trace characters like 雨 (rain) or 江 (river)
Listening Comprehension
Follow simple instructions in Mandarin related to water experiments
Understand basic descriptions of water states and properties
Speaking Practice
Describe water using simple adjectives: 冷 (lěng - cold), 热 (rè - hot)
Role-play scenarios involving water (e.g., asking for a drink)
Cultural Connection
Learn about the importance of water in Chinese culture
Introduce water-related festivals like 端午节 (Duānwǔ jié - Dragon Boat Festival)
Songs and Rhymes
Learn simple songs about rain or rivers in Mandarin
Practice rhymes that include water vocabulary
Story Comprehension
Listen to simple stories about water in Mandarin
Retell parts of the story using learned vocabulary
Writing Practice
Practice writing the character 水 (water)
Create simple pictographs combining 水 with other elements
-
A study on water relates closely to several UN Sustainability Development Goals (SDGs) and has significant implications for livelihoods. Here's how:
UN Sustainability Development Goals related to water:
SDG 6: Clean Water and Sanitation
Directly addresses water access, quality, and management
SDG 3: Good Health and Well-being
Clean water is essential for preventing water-borne diseases
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
Water is crucial for agriculture and food production
SDG 14: Life Below Water
Focuses on conserving and sustainably using water resources
SDG 15: Life on Land
Water is vital for terrestrial ecosystems
SDG 13: Climate Action
Water cycles are deeply affected by climate change
Impact of water shortage on livelihoods:
Agricultural Productivity
Reduced crop yields and livestock production
Loss of farmer income and food insecurity
Economic Impacts
Decreased industrial output in water-dependent industries
Increased costs for water in urban areas
Health Consequences
Increased risk of water-borne diseases
Malnutrition due to food scarcity and poor sanitation
Education
Children, especially girls, may miss school to collect water
Reduced learning capacity due to health issues
Social Stability
Water scarcity can lead to conflicts over resources
Forced migration from water-stressed areas
Gender Inequality
Women and girls often bear the burden of water collection
Time spent on water collection reduces opportunities for education and employment
Environmental Degradation
Overexploitation of water sources damages ecosystems
Loss of biodiversity impacts traditional livelihoods
Urban Challenges
Informal settlements struggle with water access and sanitation
Increased urban poverty due to rising water costs
Energy Production
Reduced hydroelectric power generation
Impacts on cooling systems for other power plants
Tourism and Recreation
Negative impacts on water-based tourism activities
Loss of income in tourism-dependent communities
For a PreK 1 water project, these complex issues can be introduced in simple terms, focusing on the importance of water conservation and its impact on people and the environment. Activities could include:
Learning about how plants and animals need clean water
Simple water-saving practices at home and school
Understanding that some people have to walk far to get water
Exploring how we use water in different ways (drinking, cleaning, growing food)
-
Math Standards:
Counting and Cardinality:
Students can count the number of tracks in a series up to 5.
Students can recognize and name groups of 1 to 3 objects without counting (subitizing).
Measurement and Data:
Students can compare sizes of different tracks using terms like "bigger," "smaller," and "same size."
Students can sort tracks or fossils into simple categories (e.g., by size or shape).
Geometry:
Students can identify basic shapes in tracks or fossil imprints (e.g., circles, ovals, triangles).
Students can use positional words to describe where tracks are located (e.g., next to, between, in front of).
Patterns:
Students can recognize and extend simple patterns in a series of tracks (e.g., big track, small track, big track, small track). OR bird track, mammal track etc.
-
Mandarin Literacy:
Students can recognize and say simple Mandarin words related to animals (动物, dòngwù), such as: • 恐龙 (kǒnglóng) - dinosaur • 足迹 (zújì) - footprint • 骨头 (gǔtou) - bone
Students can use basic Mandarin vocabulary to describe what they observe, such as: • 大 (dà) - big • 小 (xiǎo) - small • 旧 (jiù) - old • 新 (xīn) - new
Students can respond to simple Mandarin instructions related to the unit, like: • 看 (kàn) - look • 摸 (mō) - touch • 找 (zhǎo) - find
-
Science:
Students can identify and compare different types of tracks and traces left by animals.
Students can match common animal tracks to the correct animal (e.g., bird, cat, dog, rabbit).
Students can recognize that fossils are evidence of living things from long ago.
Students can sort objects into categories of "living" and "non-living" things.
Students can describe basic differences between tracks (e.g., big/small, many toes/few toes).
-
Goal 13: Climate Action
Students can recognize that some animals and plants from long ago no longer exist.
Students can understand that our actions can help or harm animals and their habitats.
Goal 14: Life Below Water
Students can identify tracks or traces of water animals (like fish fossils or seashells).
Students can understand that water habitats are home to many living things.
Goal 4: Quality Education
This goal is inherently supported by the unit itself, as it provides early education on environmental topics.
Students can share what they've learned about tracks and trails with friends or family.